Levodopa: Essential Precursor in Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
1. Molecular Identity
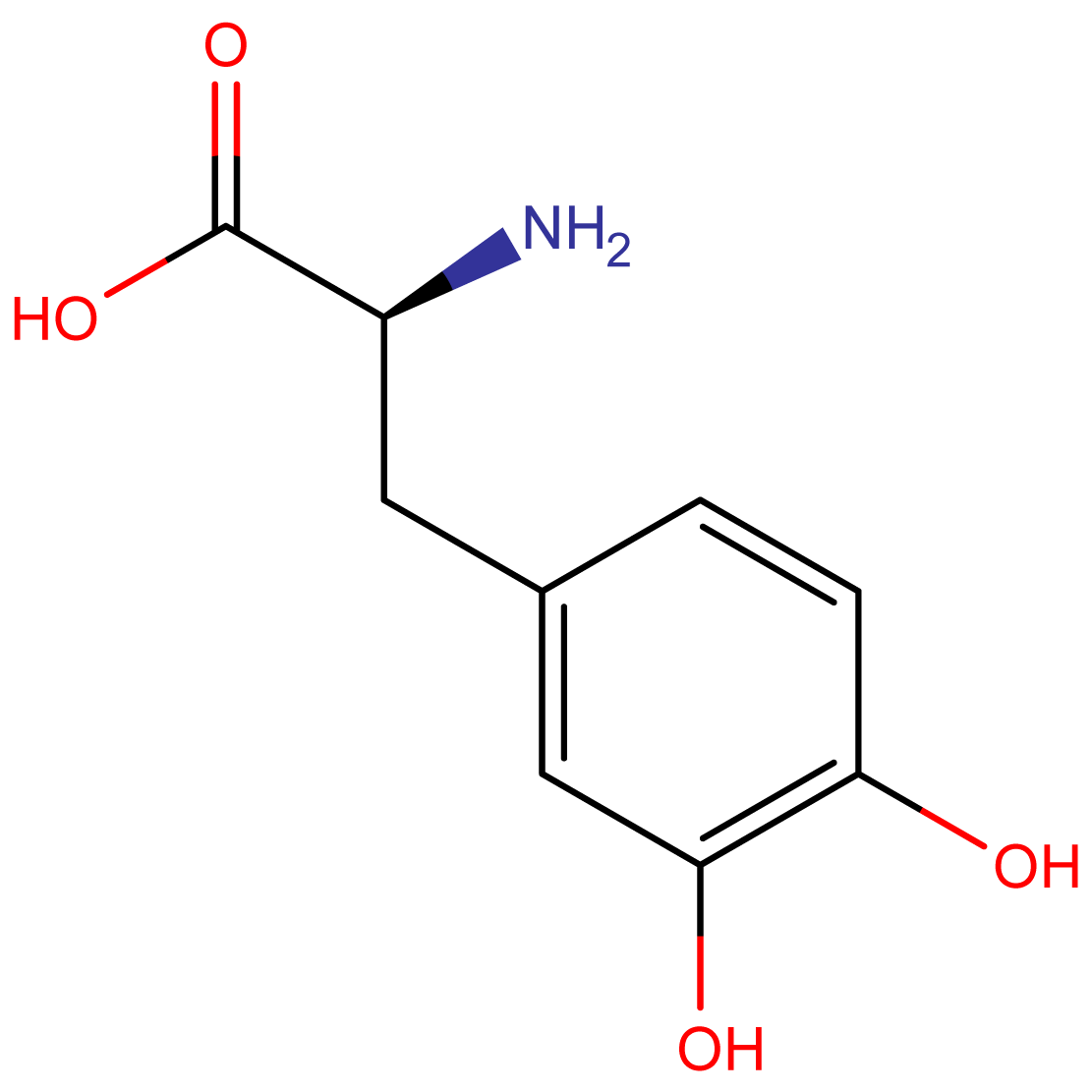
- Chemical Name: (S)-2-Amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- CAS Number: 59-92-7
- Source: Synthetic amino acid, also found naturally in certain plants
2. Biochemical Significance
Levodopa (L-DOPA) is the immediate precursor of dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and convert to dopamine makes it a cornerstone in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and a compound of significant interest in neuropharmacological research.
3. Key Therapeutic Properties
- Dopamine Precursor: Effectively increases brain dopamine levels
- Symptomatic Relief: Improves motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease
- Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration: Efficiently enters the central nervous system
- Neurotransmitter Modulation: Influences various neurological pathways
4. Potential Research Applications
- Parkinson’s disease treatment optimization
- Neurodegenerative disorder studies
- Dopaminergic system investigations
- Motor function and movement disorder research
5. Current Research Focus
Ongoing studies are investigating Levodopa’s effects on:
- Long-term efficacy and side effects in Parkinson’s treatment
- Combination therapies to enhance effectiveness
- Novel delivery systems for continuous dopaminergic stimulation
- Potential applications in other neurological disorders
6. Formulation Challenges and Innovations
Researchers are actively working on:
- Developing extended-release formulations
- Creating targeted delivery systems to minimize peripheral side effects
- Optimizing combinations with decarboxylase inhibitors
7. Regulatory Considerations
Levodopa (CAS 59-92-7) is an FDA-approved drug for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Its use in research should comply with relevant regulations and ethical guidelines for human and animal studies.
8. Future Research Directions
The scientific community anticipates:
- Advanced studies on neuroprotective potential
- Exploration of personalized dosing strategies
- Development of novel drug delivery technologies
9. Collaborative Opportunities
We invite neuroscientists, pharmaceutical researchers, and academic institutions to explore the research potential of Levodopa. For inquiries, collaborations, or to discuss how Levodopa can benefit your research projects, please contact us at sales@nstchemicals.com.
Join us in advancing neurological research with Levodopa – a crucial compound in the ongoing fight against Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders.