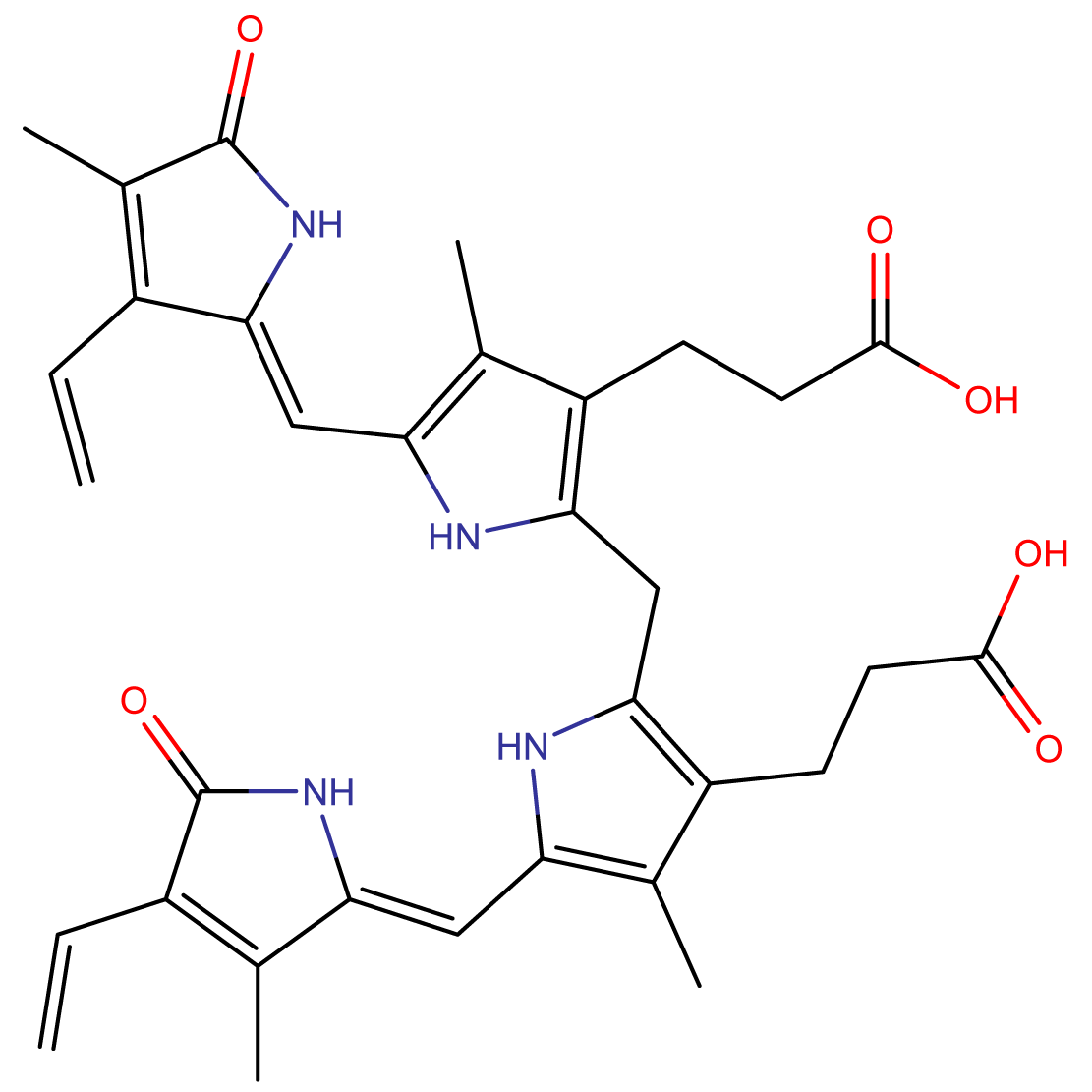
Bilirubin (635-65-4): Essential Heme Metabolite for Advanced Biomedical Research
1. Molecular Identity
- Chemical Name: (4Z,15Z)-2,3-Dihydro-2-(4-((2,3-dihydro-1,5-dihydroxy-3-oxo-2H-pyrrol-2-yl)methyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-1,19-dihydro-22H-bilindione
- CAS Number: 635-65-4
- Source: Endogenous product of heme catabolism in mammals
2. Biochemical Significance
Bilirubin (635-65-4) is a tetrapyrrole compound formed as the final product of heme degradation. Its unique molecular structure contributes to its potent antioxidant properties and its role as a crucial biomarker for liver function, making it a compound of significant interest in hepatology, neonatology, and oxidative stress research.
3. Key Properties of Bilirubin (635-65-4)
- Antioxidant: Exhibits powerful free radical scavenging activity
- Liver Function Biomarker: Elevated levels indicate potential liver disorders
- Neurotoxicity: Can be harmful at high concentrations, especially in neonates
- Photosensitivity: Undergoes structural changes when exposed to light
4. Potential Research Applications
- Liver disease studies
- Neonatal jaundice investigations
- Oxidative stress and antioxidant research
- Heme metabolism pathway studies
5. Current Research Focus
Ongoing studies are investigating bilirubin’s effects on:
- Cardiovascular disease prevention
- Neuroprotection in neurodegenerative disorders
- Anti-inflammatory mechanisms
- Biomarker development for various pathological conditions
6. Formulation Challenges and Innovations
Researchers are actively working on:
- Enhancing stability and solubility for experimental use
- Developing sensitive and specific detection methods
- Creating bilirubin-inspired antioxidant compounds
7. Regulatory Considerations
Bilirubin (635-65-4) is an endogenous compound and is primarily used in research and diagnostic settings. Its use in potential therapeutic applications would require extensive safety and efficacy evaluations to meet regulatory standards.
8. Future Research Directions
The scientific community anticipates:
- Advanced studies on bilirubin’s role in cellular signaling pathways
- Exploration of its potential as a therapeutic agent in oxidative stress-related diseases
- Development of novel bilirubin-based biomarkers for early disease detection
9. Collaborative Opportunities
We invite hepatologists, neonatologists, oxidative stress researchers, and academic institutions to explore the research potential of bilirubin. For inquiries, collaborations, or to discuss how this compound can benefit your research projects, please contact us at sales@nstchemicals.com.
Join us in advancing biomedical research with bilirubin – a crucial metabolite at the intersection of heme metabolism, liver function, and antioxidant biology.