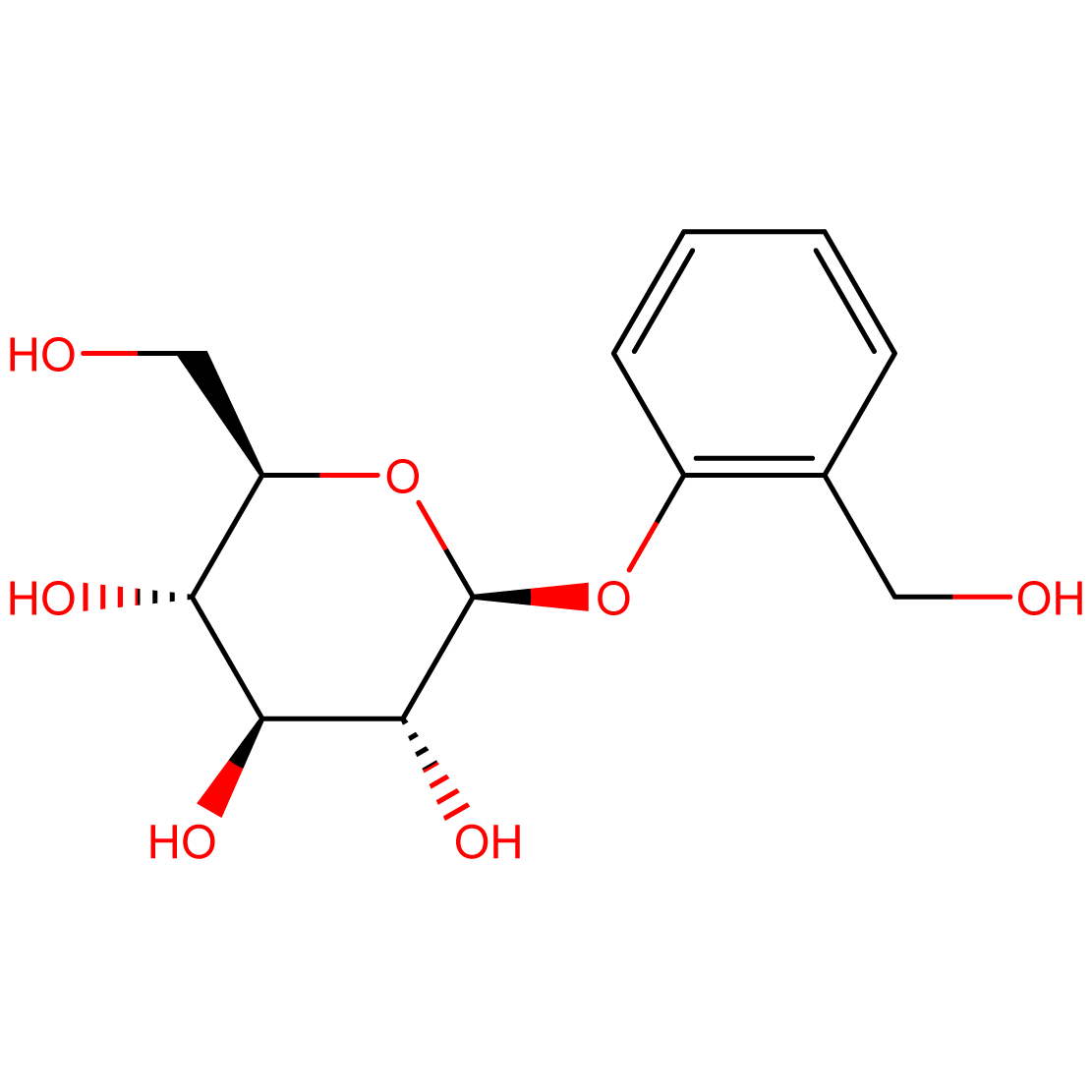
Salicin: Nature’s Aspirin Precursor
1. Molecular Identity
- Chemical Name: 2-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside
- CAS Number: 138-52-3
- Source: Naturally occurring in various species of willow tree (Salix), as well as in poplar and aspen trees
2. Biochemical Significance
Salicin is a natural glucoside that serves as a prodrug to salicylic acid. Its historical use in traditional medicine led to the development of aspirin, making it a compound of significant interest in pharmacological research and natural product studies.
3. Key Therapeutic Properties
- Analgesic: Demonstrates pain-relieving effects
- Anti-inflammatory: Exhibits ability to reduce inflammation
- Antipyretic: Shows potential in reducing fever
- Antioxidant: Possesses free radical scavenging activity
4. Potential Applications
- Pain management research
- Inflammatory disorder studies
- Fever reduction investigations
- Natural product-based drug development
5. Current Research Focus
Ongoing studies are investigating Salicin’s effects on:
- Chronic pain conditions
- Inflammatory pathways and mediators
- Cardiovascular health
- Potential synergistic effects with other natural compounds
6. Formulation Challenges and Innovations
Researchers are actively working on:
- Enhancing bioavailability and absorption rates
- Developing controlled-release formulations
- Creating stable preparations for various research applications
7. Regulatory Considerations
Salicin is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in food applications. Its use in specific therapeutic applications may require additional regulatory approval depending on the jurisdiction and intended use.
8. Future Directions
The scientific community anticipates:
- Advanced clinical trials comparing Salicin to synthetic analgesics
- Exploration of Salicin’s potential in combination therapies
- Development of novel delivery systems for enhanced efficacy
9. Collaborative Opportunities
We invite researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and academic institutions to explore the therapeutic potential of Salicin. For inquiries, collaborations, or to discuss how Salicin can benefit your research or product development, please contact us at sales@nstchemicals.com.
Join us in harnessing the power of Salicin – a natural compound bridging traditional herbal wisdom with modern pharmacological applications.