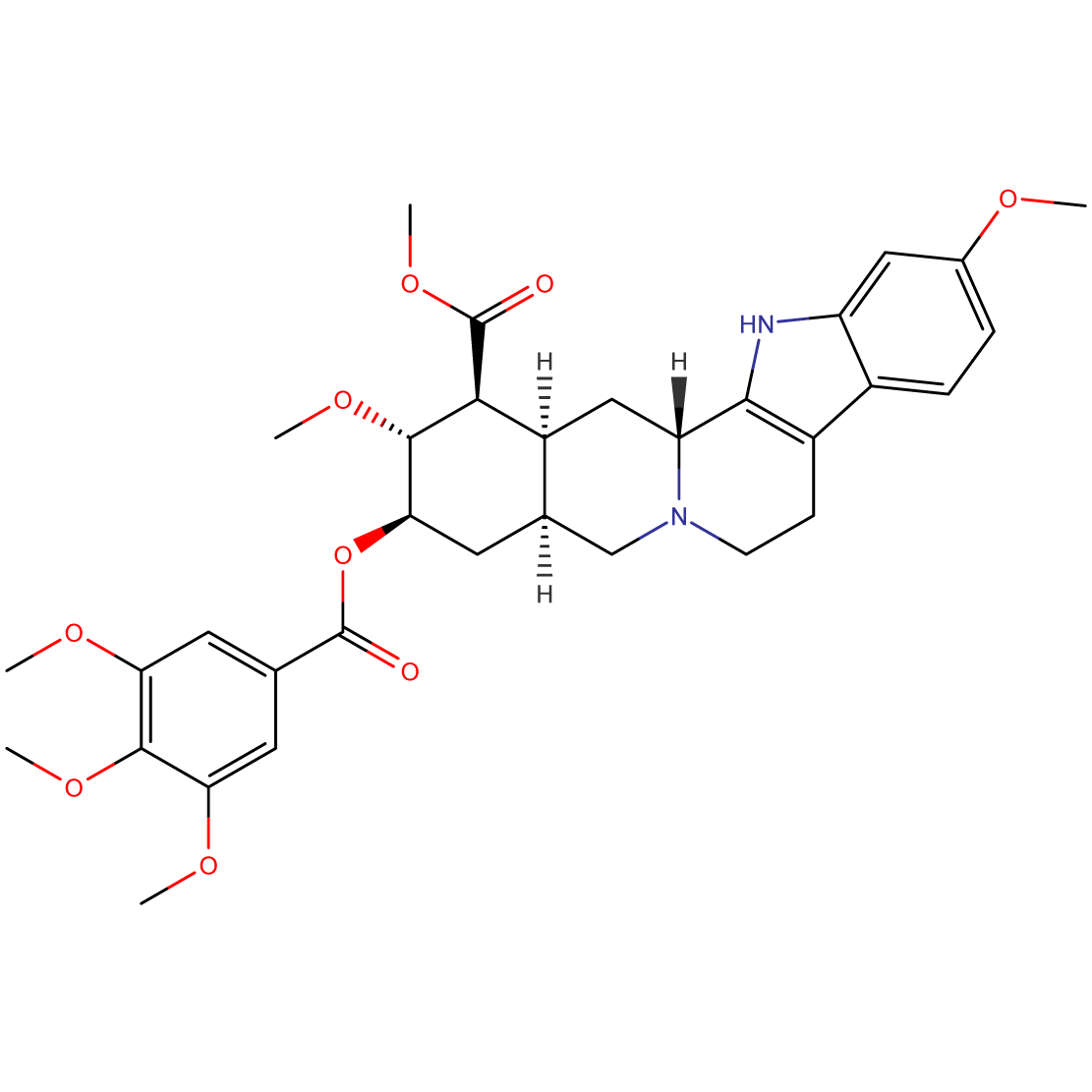
Reserpine (50-55-5): Potent Alkaloid for Advanced Neuropharmacological Research
1. Molecular Identity
- Chemical Name: Methyl (3β,16β,17α,18β,20α)-11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxylate
- CAS Number: 50-55-5
- Source: Naturally occurring in Rauwolfia serpentina and other Rauwolfia species
2. Biochemical Significance
Reserpine (50-55-5) is an indole alkaloid with profound effects on neurotransmitter storage and release. Its unique molecular structure allows it to deplete monoamine neurotransmitters, making it a compound of significant interest in neuropharmacology and psychiatric research.
3. Key Properties of Reserpine (50-55-5)
- Monoamine Depletor: Reduces stores of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine
- Antihypertensive: Demonstrates potent blood pressure-lowering effects
- Neuromodulator: Alters neurotransmitter dynamics in the central nervous system
- Sedative: Exhibits calming and tranquilizing properties
4. Potential Research Applications
- Neurotransmitter storage and release studies
- Hypertension and cardiovascular research
- Psychiatric disorder investigations
- Animal models of depression and anxiety
5. Current Research Focus
Ongoing studies are investigating reserpine’s effects on:
- Vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) function
- Neurodegenerative disease mechanisms
- Mood disorder pathophysiology
- Autonomic nervous system regulation
6. Formulation Challenges and Innovations
Researchers are actively working on:
- Developing targeted delivery systems to minimize systemic effects
- Creating controlled-release formulations for research applications
- Exploring reserpine analogs with enhanced selectivity
7. Regulatory Considerations
Reserpine (50-55-5) is approved as a prescription drug in some countries for hypertension. Its use in research settings is subject to regulatory oversight due to its potent pharmacological effects.
8. Future Research Directions
The scientific community anticipates:
- Advanced studies on reserpine’s role in neurotransmitter dynamics
- Exploration of its potential in novel psychiatric research models
- Investigation of long-term neuroplasticity effects
9. Collaborative Opportunities
We invite neuropharmacologists, psychiatrists, and academic institutions to explore the research potential of reserpine. For inquiries, collaborations, or to discuss how this compound can benefit your research projects, please contact us at sales@nstchemicals.com.
Join us in advancing neuropharmacological research with reserpine – a powerful alkaloid at the forefront of neurotransmitter and psychiatric studies.